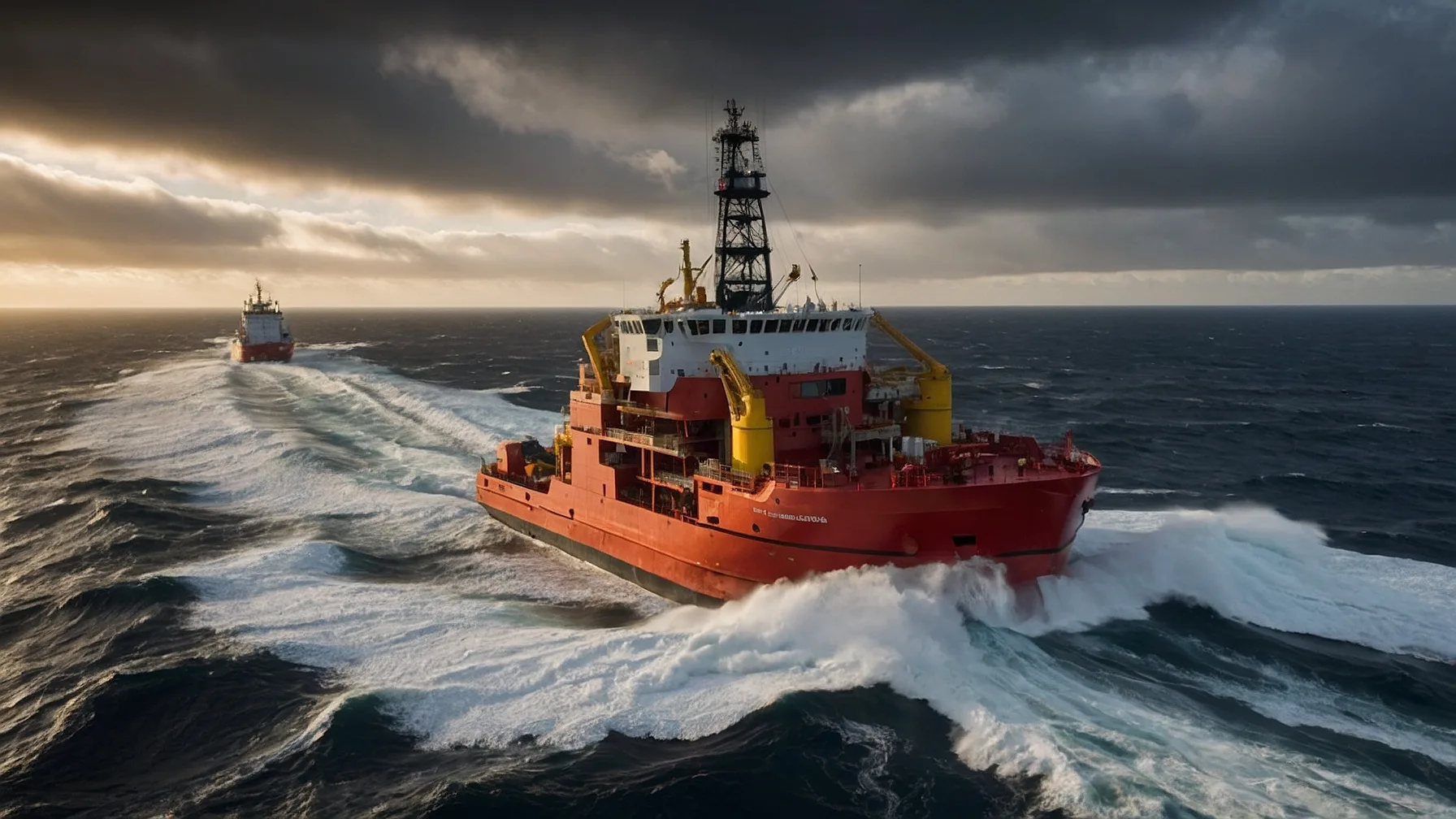
Have you ever wondered what is an anchor handling tug supply vessel ?An Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel (AHTS) is one of the most vital and versatile vessels in offshore oil and gas exploration. Anchor Handling Tug Supply (AHTS) vessels are designed for a wide range of complex and critical functions, making them indispensable in offshore operations. These vessels are not only equipped for anchor handling, but also for towing large offshore structures, transporting essential supplies like fuel, food, and equipment to remote platforms, and even performing firefighting duties in emergency situations.
AHTS vessels are vital for maintaining the safety, efficiency, and success of offshore drilling, production, and exploration activities. Their versatility ensures that offshore operations run smoothly, whether it’s securing a platform in place, providing crucial supplies, or responding to emergencies. As such, AHTS vessels play a central role in safeguarding both human lives and the continued productivity of offshore industries.
Table of Contents
What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel ?
The role of What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel primarily revolves around the safe and efficient installation of offshore drilling rigs. These vessels are required to handle extremely heavy anchors, sometimes weighing as much as 30 tons or more. To achieve this, What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel are outfitted with high-powered winches and large cranes, capable of lifting, handling, and securing anchors that hold drilling platforms in place.
They also have a range of other functions. For example, What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel are capable of transporting essential goods such as fuel, food, and equipment to offshore rigs, all while maintaining the necessary operational readiness for emergency situations. The vessels are also equipped with dynamic positioning (DP) systems that enable them to maintain a fixed position without relying on anchors, which is crucial in deep water operations.
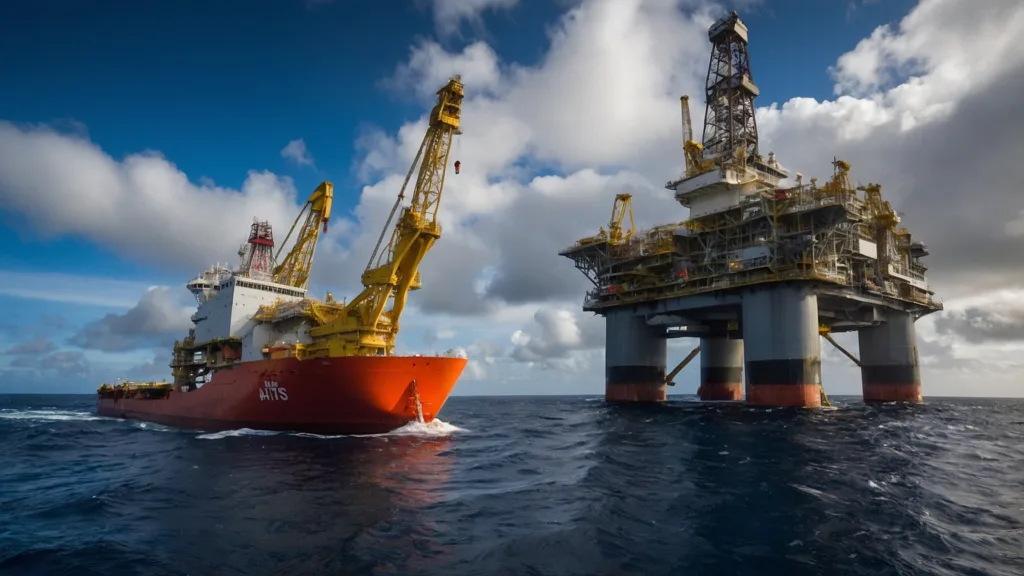

Power and Size of AHTS Vessels
AHTS vessels tend to be significantly larger than standard tugboats, ranging from 50 meters to over 80 meters in length. Their power comes from the immense engines—often several thousand horsepower—providing them with the strength needed to perform tasks like towing floating oil platforms and even acting as emergency response vessels.
In addition to power, AHTS vessels are designed to withstand harsh offshore environments. Their robust construction includes reinforced hulls, ensuring that the vessel can endure collisions, ice, and rough seas without compromising structural integrity.
What Are Tugboats?
The tugboat is often considered the workhorse of the maritime world. What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel is a versatile vessel designed primarily to tow or push larger ships and barges, assisting in navigation through narrow, confined spaces, or maneuvering heavy vessels in busy harbors.
What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel are typically smaller than the vessels they assist, but they are exceptionally powerful for their size. Some of the most powerful tugboats have engines producing over 10,000 horsepower, enabling them to tow much larger vessels. These vessels are engineered for agility and speed, crucial qualities for working in tight spaces or during challenging weather conditions.
In fact, What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel are often considered a ship’s “guardian angel,” ensuring that the vessel can be navigated safely to port, in and out of docks, or through challenging waterways. They can also be used for firefighting, oil spill containment, and emergency salvage operations.
Also Read : How Does a Ship Anchor Work? 7 Ultimate Facts About Ship Anchors
Different Types of Tugboats
Tugboats are highly specialized vessels, designed to perform a variety of tasks. Their roles can be broken down into several types based on their purpose and operation.
Harbor Tugboats :
These are the most common types of tugboats seen in port areas. Harbor tugboats are used for maneuvering ships into and out of docks, turning large vessels around in tight spaces, and assisting with the safe navigation of ships through narrow channels. These tugboats are typically smaller, designed for agility rather than power.
Offshore Tugboats:
Larger and more powerful than harbor tugboats, offshore tugboats are typically used in deep-sea operations. Their main function is to tow oil rigs, barges, and other large structures between different offshore locations. These tugboats need to be capable of enduring rough sea conditions while towing massive objects.
Icebreaking Tugboats:
These tugboats are specifically designed to navigate icy waters. Their hulls are reinforced to prevent damage from the pressure of thick ice, enabling them to break through frozen waters to allow the passage of other ships.
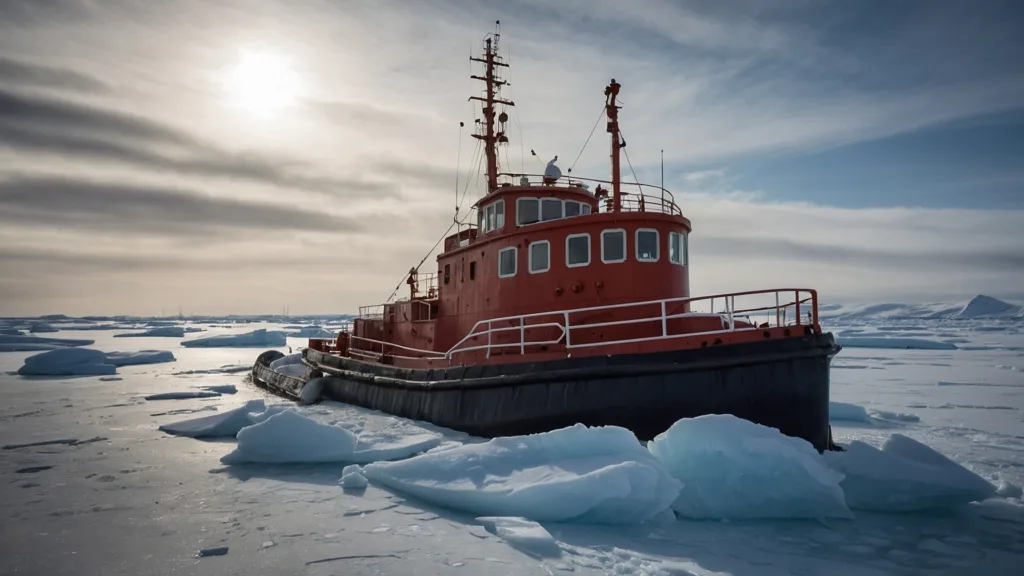

Salvage Tugboats:
Used in emergency situations, salvage tugboats are designed for rescue operations. They assist distressed vessels, help tow them to safety, or even prevent a sinking ship from going under.
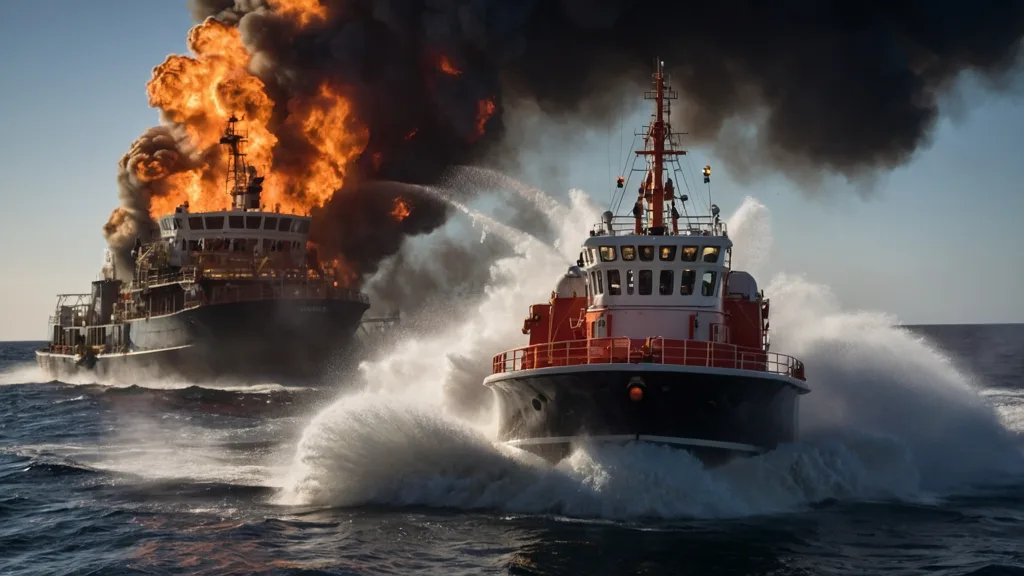
Firefighting Tugboats:
In addition to their primary role of towing, these tugboats are equipped with heavy-duty water cannons and are often used in ports or offshore rigs for firefighting operations.

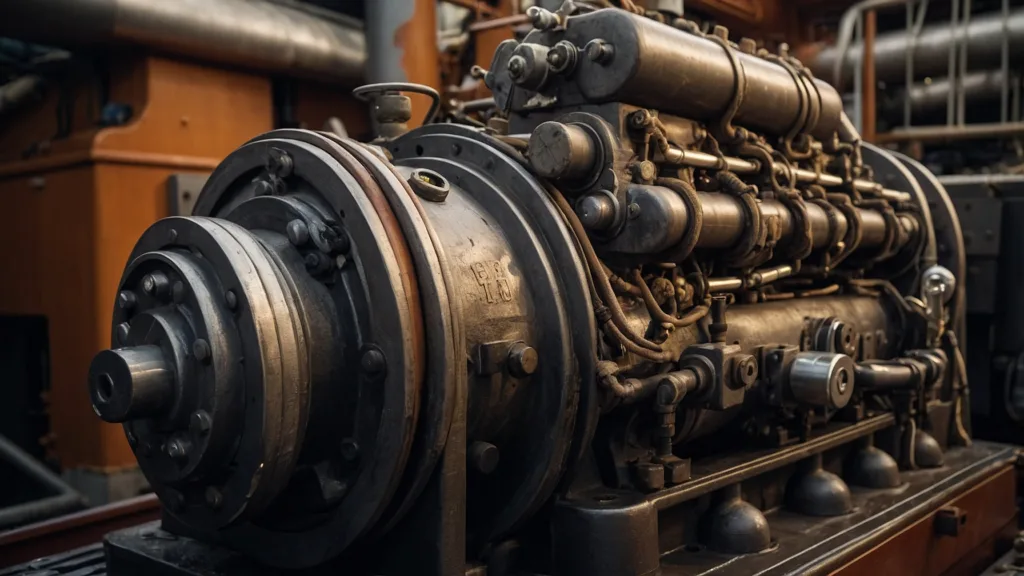
The Mechanics of Tugboats: Tugboat Engines and Power Systems
The tugboat engine stands as one of the most critical and powerful components of the vessel, providing the necessary force to carry out a wide variety of demanding tasks. These engines are designed to generate an immense amount of horsepower, often exceeding 10,000 horsepower in larger tugboats, allowing them to perform heavy-duty operations like towing massive vessels, pushing barges, or assisting ships in maneuvering through congested harbors.
Given the high-power demands, tugboat engines are typically diesel-powered, with diesel engines prized for their robustness, reliability, and efficiency, especially in harsh and challenging marine environments. Diesel engines are particularly suited for these tasks, delivering the power required for continuous high-load operations in all conditions. However, newer models are increasingly incorporating hybrid engines, which combine both diesel and electric power, providing a balance of efficiency, reduced emissions, and improved fuel economy. These hybrid systems are becoming more popular as the industry moves toward greener solutions in an environmentally conscious world.
Also Read : What Is Docking? 9 Best Things You Must Know About Docking
Tugboats also rely heavily on azimuth thrusters—rotatable propulsion units that allow the vessel to move in any direction. These thrusters provide exceptional maneuverability, allowing tugboats to push or pull vessels from virtually any angle. This ability is crucial when operating in tight harbors or narrow channels, where the ability to position and control the tugboat precisely is of utmost importance. Azimuth thrusters make tugboats particularly effective in crowded ports, assisting in navigating large vessels into docks or reversing and turning them in limited spaces.
Another distinctive and noteworthy feature of tugboat engines is their capability to sustain high loads over extended periods of time. Unlike most other types of vessels, tugboats are built to endure the intense stresses of constant towing, pushing, and maneuvering, which requires continuous, high-performance output from their engines. These engines are designed to handle not just the weight of the vessels they tow but also the stresses of unpredictable and often rough sea conditions, ensuring that the tugboat can keep performing at a high level even under the most demanding operational scenarios. The durability of the tugboat engine is a key factor in ensuring the vessel remains operational for long hours without compromising its power or functionality.
Why Do Tugboats Spray Water?
At times, when you see a tugboat operating, you may notice it spraying large amounts of water from its hoses. This is a common feature, particularly in harbor operations. There are several important reasons why tugboats engage in this action:
Firefighting and Safety:
One of the primary reasons tugboats spray water is to act as a firefighting measure. Many tugboats are equipped with firefighting systems that can discharge massive quantities of water to extinguish fires or prevent them from spreading. This is especially important in areas like oil rigs or ships carrying flammable materials.
Engine Cooling:
Tugboats are often subjected to extreme operating conditions, especially in the summer months or when working in hot environments. Spraying water helps cool down the engine and other critical systems, ensuring that the tugboat does not overheat and can continue its work efficiently.
Protecting the Ship from Sparks:
Tugboats may also spray water as a protective measure when towing or assisting a ship, especially in high-risk environments. The spray can help protect the ship from any sparks that may arise from friction or mechanical issues.
Signaling and Display:
Tugboats sometimes spray water as a celebratory or signaling gesture. It’s a common sight at maritime festivals or during significant operations, symbolizing the completion of a task or a job well done.
The Cost of Tugboats: How Much Do Tugboats Cost?
The cost of tugboats varies widely depending on their size, design, capabilities, and purpose. For example, harbor tugboats, which are smaller and less complex, tend to cost significantly less than specialized offshore tugboats or anchor handling vessels.
Harbor Tugboats:
Small tugboats designed for harbor operations can cost between $1 million to $5 million. These vessels are relatively simple compared to offshore tugboats, designed primarily for pushing and pulling vessels in port areas.
Offshore Tugboats:
For larger offshore tugboats, particularly those used for towing oil rigs or large ships, prices range from $5 million to $12 million. These vessels require more powerful engines, reinforced hulls, and advanced systems to deal with the demands of offshore operations.
Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessels (AHTS):
These highly specialized vessels can cost significantly more, ranging from $20 million to $40 million or more. Their complex systems for anchor handling, towing, and offshore supply operations make them some of the most expensive vessels on the market.
Salaries and Careers in the Tugboat Industry: How Much Do Tug Boat Captains Make?
How Much Do Tug Boat Captains Make? The tugboat industry offers well-paying career opportunities, especially for experienced tugboat operators and captains. The role of a tugboat captain comes with substantial responsibility, as they are in charge of safely maneuvering large vessels, performing complex towing operations, and ensuring the safety of their crew.
Tugboat Operator Salary:
The salary of a tugboat operator can vary depending on their experience, the type of tugboat they operate, and the location in which they work. On average, a tugboat operator earns between $45,000 and $70,000 per year. More experienced operators can earn up to $85,000 annually, especially if they are working on offshore tugboats or for large shipping companies.
Tugboat Captain Salary:
Tugboat captains earn higher salaries due to their increased responsibility. The salary range for a tugboat captain is typically between $80,000 and $150,000 per year. However, captains with several years of experience or those working on offshore tugboats in dangerous conditions can earn more, with some captains earning as much as $200,000 or more annually.
How Much Do Tugboats Cost?
Tugboats are expensive investments, but they are crucial for maritime and offshore operations. The cost of tugboats can vary significantly depending on their design and intended use. Smaller harbor tugboats typically cost between $1 million and $5 million, while more specialized vessels such as anchor handling tug supply vessels (AHTS) can cost anywhere from $20 million to $40 million. Prices depend on several factors, including the vessel’s size, engine power, features, and purpose.
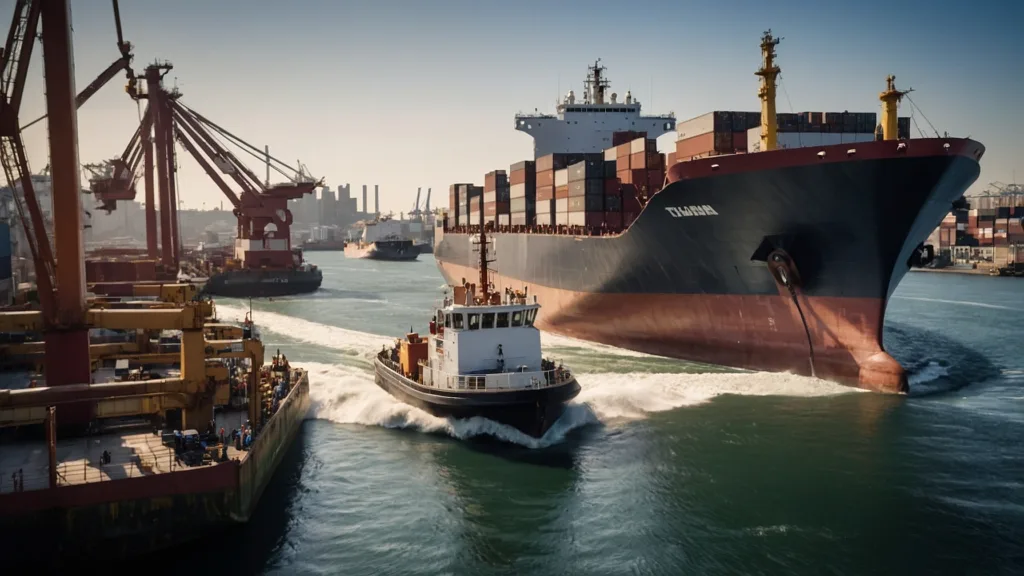

The Global Market for Tugboats and Anchor Handling Vessels
The tugboat industry is a key part of global maritime trade and offshore activities. As international trade grows, and as offshore oil and gas exploration expands, the demand for tugboats is expected to increase. The global market for tugboats, particularly in regions with active ports or offshore drilling, continues to expand. Countries like the United States, Canada, Brazil, China, and the United Arab Emirates have strong tugboat markets, driven by large harbors, oil rigs, and other maritime infrastructure.
Additionally, as the world focuses on sustainability, there is growing interest in environmentally friendly tugboats. The industry is exploring the use of hybrid engines and clean fuels, which reduce emissions while maintaining the tugboats’ powerful capabilities. This eco-friendly approach will likely shape the future of tugboats.

Conclusion
Tugboats, and specifically What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel, play a vital role in the maritime and offshore industries. Whether assisting massive ships in harbor or performing complex tasks like towing oil rigs across vast oceans, What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel are the unsung heroes that keep global trade and offshore operations running smoothly. With their specialized engines and advanced maneuverability, these vessels are designed to tackle the toughest challenges in some of the most extreme environments on Earth.
Understanding the different types of tugboats, their key functions, and their costs offers valuable insight into why these vessels are such indispensable assets to the maritime industry. With cutting-edge designs and innovations from manufacturers worldwide, the tugboat industry continues to evolve. As new technologies emerge, there’s a shift toward more eco-friendly solutions, including hybrid engines and cleaner fuels, which could shape the future of What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel.
For those pursuing a career in this field, tugboat operator salaries and captain wages are highly competitive, especially for those in specialized roles like offshore operations. However, this line of work requires skill, experience, and the ability to thrive under pressure in challenging conditions.
At the heart of it, What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel aren’t just machines—they’re a testament to human ingenuity and resilience. As we look toward the future of global trade, maritime safety, and offshore exploration, one thing is clear: What is an Anchor Handling Tug Supply Vessel will continue to be indispensable, ensuring the world’s maritime operations stay afloat, no matter the storm.
FAQS
What are the different types of anchor handling?
Anchor handling can be manual, where the crew uses ropes or winches; mechanical, which involves machinery like winches or tugboats; or automated, where systems manage the deployment and retrieval of anchors efficiently.
What is the difference between AHT and AHTS?
The difference between AHT and AHTS is:
AHT (Anchor Handling Tug): A vessel designed primarily for handling anchors, including towing and positioning rigs. It focuses mainly on anchor handling and towing tasks.
AHTS (Anchor Handling Tug Supply): A more versatile vessel that not only handles anchors and towing but also supplies goods and equipment to offshore platforms. It combines the features of an AHT with the capability to transport supplies.
What is the capacity of a tug?
The capacity of a tug typically refers to its bollard pull, which is the maximum force it can exert while towing. Tug capacities can vary based on size and type, but generally:
Small Tugs: Around 10–30 tons of bollard pull.
Medium Tugs: 30–60 tons of bollard pull.
Large Tugs: 60–150 tons or more of bollard pull, especially those designed for offshore operations.
Why do cruise ships use tug boats?
Cruise ships use tugboats primarily for maneuvering in and out of harbors or ports. Tugboats assist with:
Shifting the ship’s position: They help guide the cruise ship safely when docking or undocking, especially in tight spaces or when the cruise ship is too large to maneuver easily on its own.
Providing extra power: Tugboats offer additional power to ensure safe navigation, particularly in challenging weather conditions or when the port has strong currents or wind.
Assisting with docking: They help the cruise ship align with the dock, ensuring precise and safe docking procedures.
What is the purpose of a tug vessel?
A tug vessel’s main purpose is to assist in maneuvering and towing other ships, especially in tight or congested waters. They help with docking, undocking, and navigating harbors, and can provide emergency support when needed.


